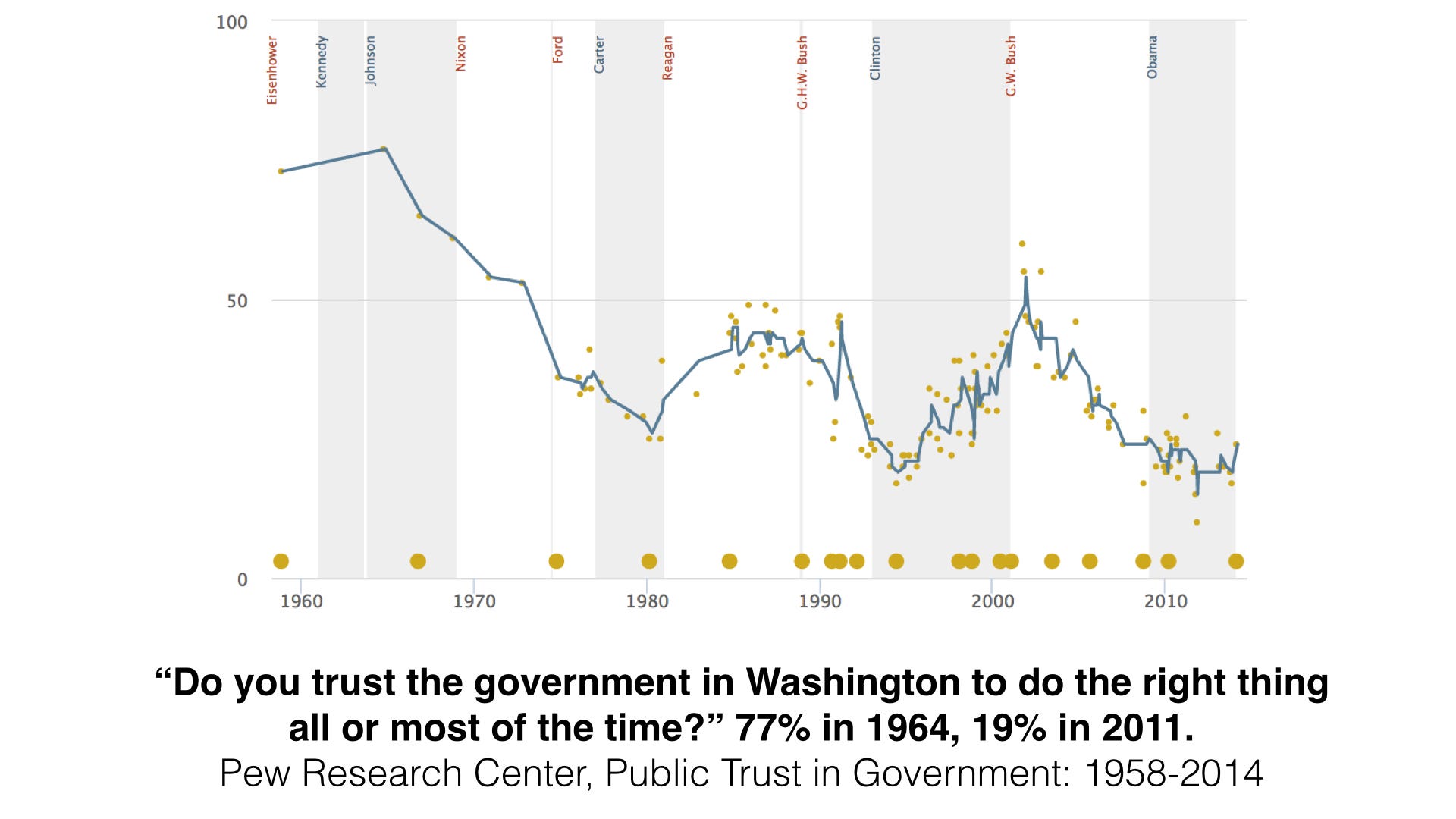
Originally posted on the Aspiration blog
After HumTechFest and the Humanitarian Technology Innovation Conference, I headed up to Toronto for the Doctors Without Borders (Médecins Sans Frontières / MSF) Canada Logistics Day. This is a day where MSF showcases and explores the ways they currently (and potentially could) do logistics. This happens in tandem with the Clinical Day, where the doctors, nurses, and other clinicians of MSF share their technology and practices. I have been a big fan of MSF for years — their delivering basic human services into regions generally abandoned by anyone else shows a level of dedication and gumption I find admirable. Medical service delivery to these areas comes with challenges even beyond standard response. Public attention has often waned, leaving a gap in funding, donations, and international accountability. Stigma is often attached to those gaining access to basic human rights, as MSF provides medical care to civilians and militants from all sides of a conflict. Many of these regions are extremely remote. The doctors and nurses delivering these services are called medics, and the folk who back up the medics are logisticians, sometimes called “Logs.” Both sets work remotely for some tasks, while other tasks require them to be in the field. The set of Logs and Clinicians in the field and remote are linked together through communication and practice, often facilitated through technology.

One of the reasons I see MSF as so amazing is because everything they do puts the patients first. The rest of their logistics, technology, and even governance systems are designed outwards from that. Any new technology is assessed in a highly pragmatic way including questions like “what impact is it likely to have?”, “what is the failure mode?”, “who is already doing this?”, “is it worth the overhead of asking skilled practitioners to learn this new thing?” It was from this progression to the the Plateau of Productivity in the hype cycle that we looked at 3D printing and then did an overview of many different technologies, including contributing to our ecosystem map of the digital response space.
An honest look at 3D Printing
I have to admit I am hugely skeptical of the promise of 3D printing. While I lived in Seattle, there was a friendly competition between Mark Ganter at UW in what strange materials he and his students could make work through proprietary machines versus the hacked-together machines themselves produced out of Metrix Create:Space. This framed my understanding for what intellectual property battles were being fought around machines and material, how to think about material science as related to structural integrity, and what (if any) actual utility beyond prototyping 3D printing might provide. So when my host Chris Houston at MSF indicated 3D Printing was to be a topic at MSF Log Day, I balanced my desire to be skeptical with my trust that MSF is made up of realists. I was not disappointed.
Manufacturing
Let us say you are a field practitioner working at an MSF hospital in Afghanistan. If the brackets on a baby incubator break, the entire expensive and needed piece of equipment becomes a doorstop because one of the walls that would keep the baby from falling out will not stay up. To work with your Logs to get a new set of brackets possibly requires
- order forms to be filled out with specifications,
- for that order to fit into other work flows,
- for the company to be willing and able to produce you new ones within a decent time frame and budget,
- shipping those tiny pieces in with massive amounts of other goods (meaning what box it goes in matters so you can find it later),
- those boxes likely getting held up at customs for an unknown amount of time, and
- needing someone to figure out how to swap in the new working parts,
- (often on equipment which is highly proprietary).
This can take weeks if not months (if it happens at all). All that time, there is not a safe place for babies you are delivering and care taking.
Field Ready (as represented by Eric James) is helping field practitioners both with those one-off items through 3D printing and with relying less on an international supply chain. By putting engineers and industrial designers in the field with production skills and tools, conversations open up about what can be manufactured locally — with 3D printers, desktop milling machines, laser cutters, and through pre-existing local facilities. Someday there may be no need to order 20,000 buckets from Geneva and wait for them to be made, shipped, and clear customs when there is a local bucket manufacturer. This would also keep funding and capacity local. 3D printing is shiny and new enough that it opens up these conversations about what can be made more locally and why (or why not), whether it is with a 3D printer or in a manufacturing center.

Look what we found in Nepal… A giant laser cutter! We helped @KarkhanaN volunteers learn how to maintain it today.

68:56 AM – Dec 13, 2015Twitter Ads info and privacySee Field Ready’s other Tweets
I am excited about this Field Ready because they are training up locals on the equipment, increasing technical capacity in-region. They are working to keep international aid money local, as well as strengthening those production ties to the international response scene. And they are honest about their abilities and intentions.
Prosthetics
Another use case which is worth the fickle nature of 3D printers and works within the structural integrity of the objects they produce is prosthetics. The creation of prosthetics is a time consuming and artisanal practice, requiring weeks to produce something which a child might outgrow within months. By introducing new scanning and production techniques, well-fitting prosthetics can be produced in days and at significantly less cost. This means those in need are more likely to stick around for the process, and are more likely to have better fitting pieces (which means healthier physiology) over the course of their lives.
Dan Southwick of the Faculty of Information (supervisor is Matt Ratto) provided a reality check on both of these promises by giving a very blunt overview of both the limitations on 3D printers and the contexts into which they are deployed. 3D printers are fickle, needing what is closer to a lab (controlled) environment than what a humid, buggy, and high-stress field environment might be capable of maintaining. A group he and Matt have worked with, Nia Technologies, encountered a girl wanting a second left foot as her prosthetic, as the only right foot available was not a skin tone match, and there is a cultural stigma with a missing limb in that region. While a 3D printer could have printed out a new one, knowing to bring a variety of colors for printing material is important. The culture and environment in which we work matters, and cannot be glazed over. Computer Numeric Control (often just called “CNC”) machines like 3D printers and milling machines were also created to get people out of the chain of production, as people are unpredictable. Rather than follow this pattern of pushing people out of the process, the Critical Making Lab has worked to involve them. This also maintains a long chain of knowledge and increases local capacity.
These pragmatic and committed individuals are working hard, often together, in order to ease the complications in the field by MSF practitioners.
The rest of the day
But the day was not even over yet. Brains and bellies full, we dove into the end of the day with a rapid review of other technologies MSF had been making use of for the past year, including telemedicine, mapping, mobile diagnostic tools, and an MSF app.
Telemedicine
Human beings are complex, and the things that can go wrong with our bodies are hugely diverse. When working in the field, you may be one of only a few medics for hours and hours, and the special cases which crop up can be far outside your knowledge. There are no specialists to send someone to. Store and forward is a way to benefit from specialists who are far away. Images and descriptions of cases can be sent outward for either verification (it is comforting to have someone else say “yes, that is fatal” when you would otherwise be the only person who could make that call) or diagnosis and suggested treatment for something you have never seen or read about. MSF has been using this system for a couple years now, to great success. Each response takes a few hours, so your patient is often still present for response and treatment.
Another form of telemedicine has to do with increasing capacity through ongoing communication between emerging local practice and clinicians elsewhere. More real time, this is about conversation and skill building rather than edge cases and verification. I am excited to see both models being deployed, and how it starts to cover the complicated vastness of medical service.
Mapping
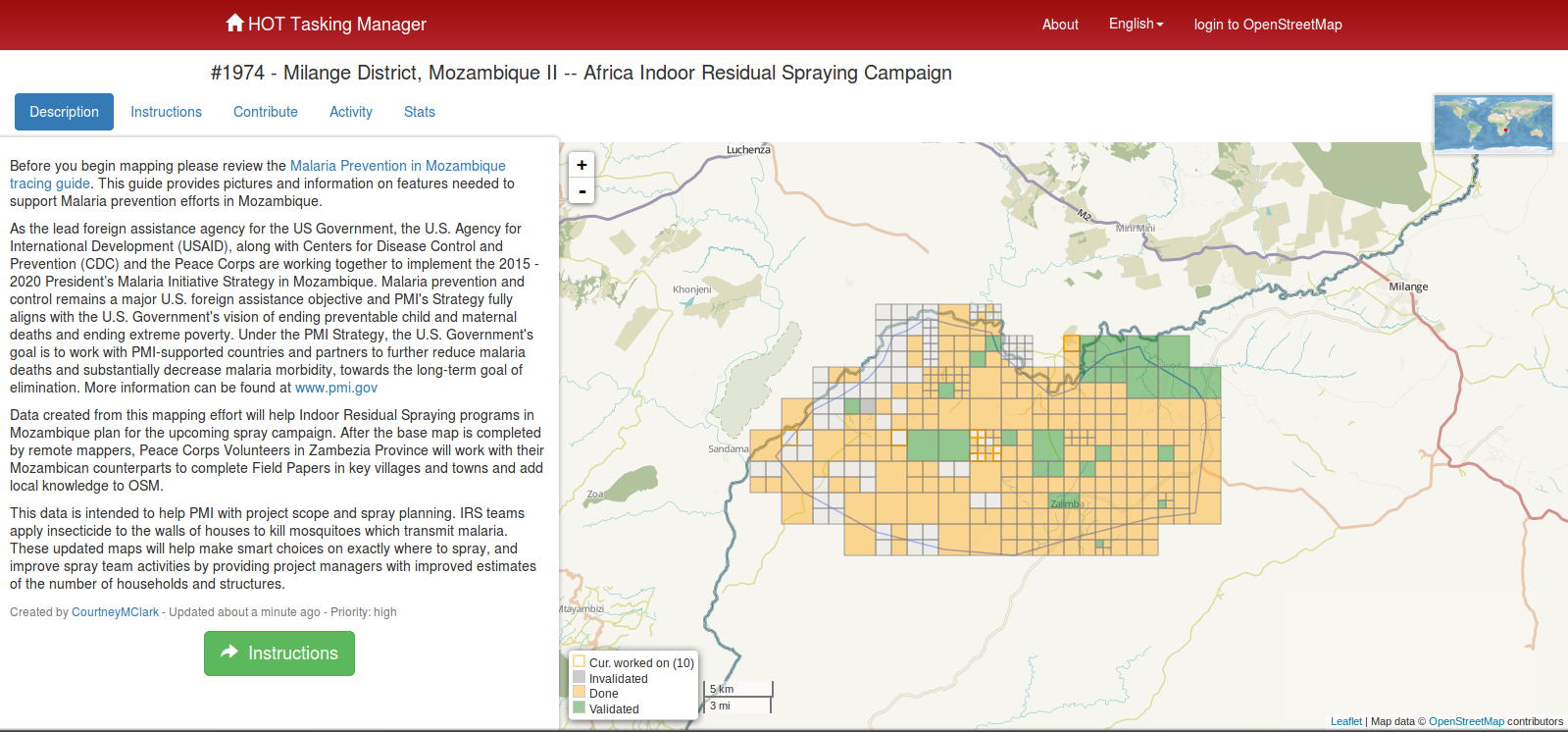
Knowing where to go relies on local knowledge and maps. Some parts of the world are not even mapped! Using satellite imagery, MSF has been working with Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT) and the Red Cross on mapping these regions which have not been mapped before in a program called Missing Maps. Digital volunteers review satellite imagery and trace objects likely to be houses or farms, which can then be reviewed in service delivery plans to make sure more people are being reached. (Side note that the map-tile categorizing tool Map Swipe which folds into Missing Maps did a user test at our digital responders’ meetup on June 16th.)
Mobile Diagnostic Tools
Medical equipment is bulky, expensive, and often single-purpose. With more and more sensors available via open hardware, smart phones, and wearables, MSF clinicians are experimenting with the possibility of other diagnostic tools. We heard from someone who was working in a region with higher-than-normal rates of epilepsy. In a “normal” hospital, the patients would be diagnosed by wearing an EEG cap attached to a bulky and expensive piece of equipment that would analyze the brain activity. But she was now able to process the data directly on her smart phone, eliminating a single-purpose piece of equipment which is expensive, has to go through the supply and logistics chain, and is just as prone to breaking as anything else.
Guidance mobile app
MSF has a lot of guides for various parts of their practice, but these are in paper format and often are either locked in a cabinet or are over-worn from use. It is not searchable, and any given clinic may not have the whole set in the most recent version. Asking forgiveness rather than permission, a set of MSF-ers transferred this knowledge into searchable and cross-linked information in a smartphone application. It has since been expanded to include telemedicine aspects and the layout of clinics. The use analytics show where training might be lacking, or where an outbreak may be happening. They are using that data to improve their overall feedback loops.
A web of technologies
All of this technology comes together in a web of communication and practice between clinicians and logisticians, often as facilitated by technology. Commitment to the end user, interoperability, and ease of use are the core components to these various technologies easing the suffering of others, rather than weighing practitioners down even further. Aspiration is eager to see how our ecosystem map and ongoing work in the digital response space can help (or at least not get in the way of) these efforts from Doctors Without Borders.